Then it may be seen that xy' = dy/dt and (x^2)y'' = (d^2/dt^2)y (dy/dt) The equation becomes (D^2 2D 1)y = (1e^t)^(2), where the operator D denotes differentiation with respect to t The homogeneous equation corresponding to the above equation is (D^2 2D 1)y = 0,
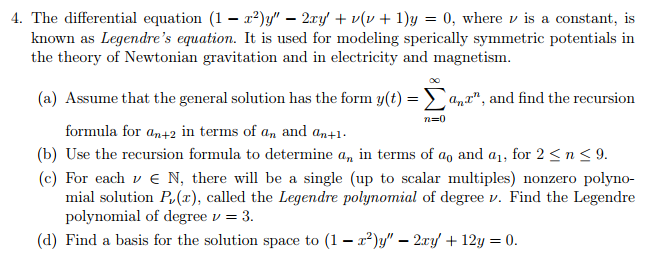
(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0-Share It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 1 vote answered by Vikash Kumar (260k points) Best answer Given differential equation is Hence general solution is ← Prev QuestionSimple and best practice solution for x^22xyy^21=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework
(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  | |
 |  | 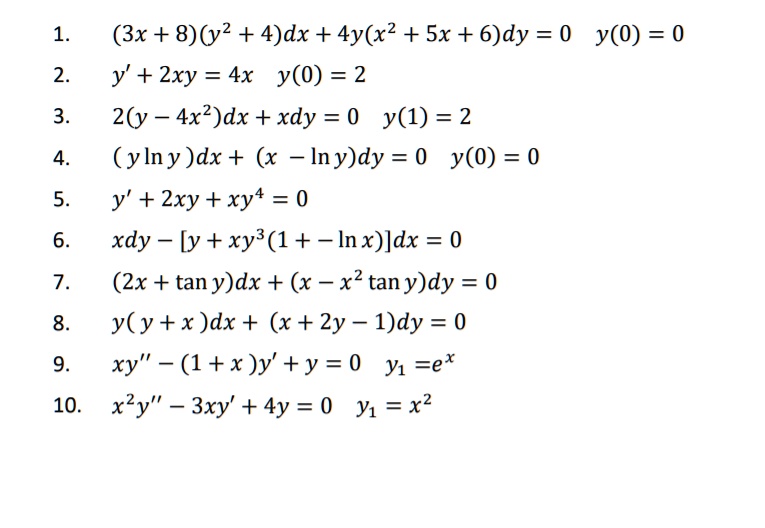 |
 |  | |
「(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | 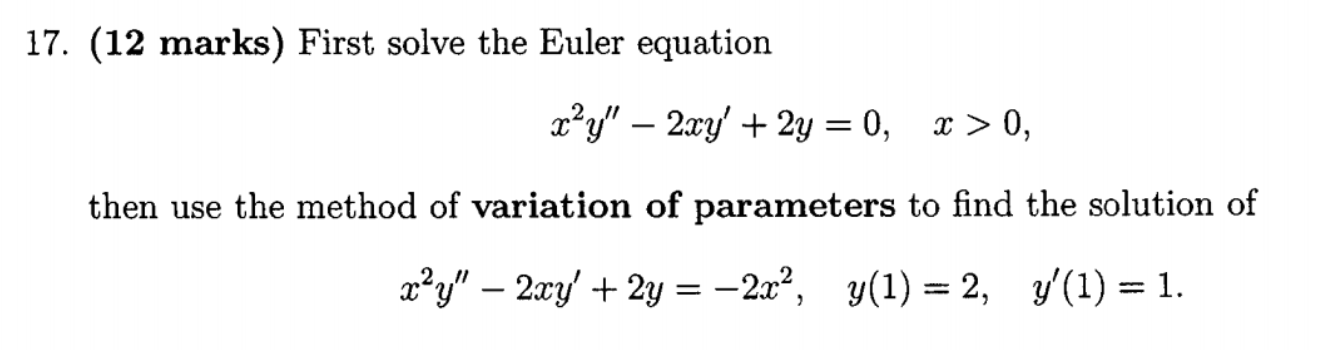 |
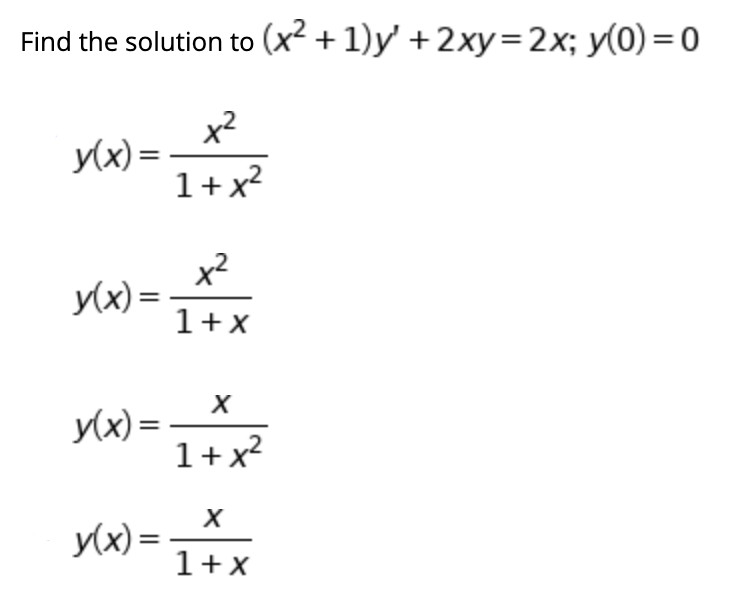 | 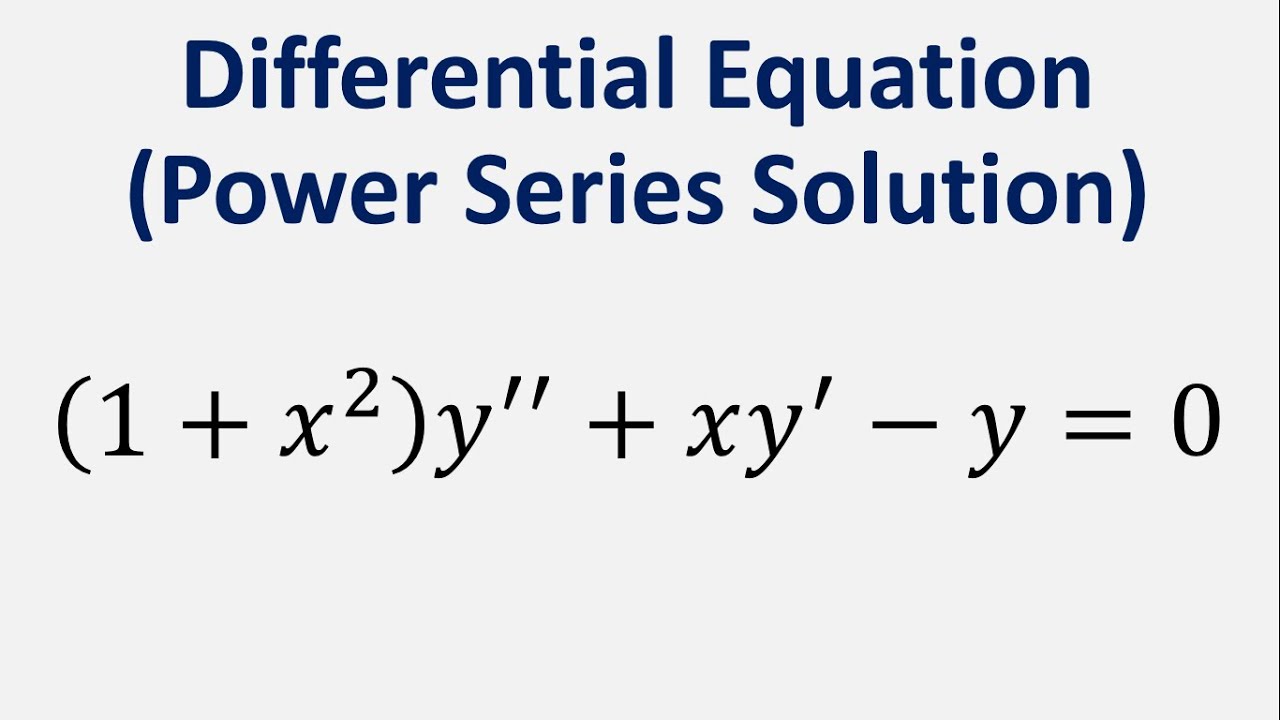 | |
 | 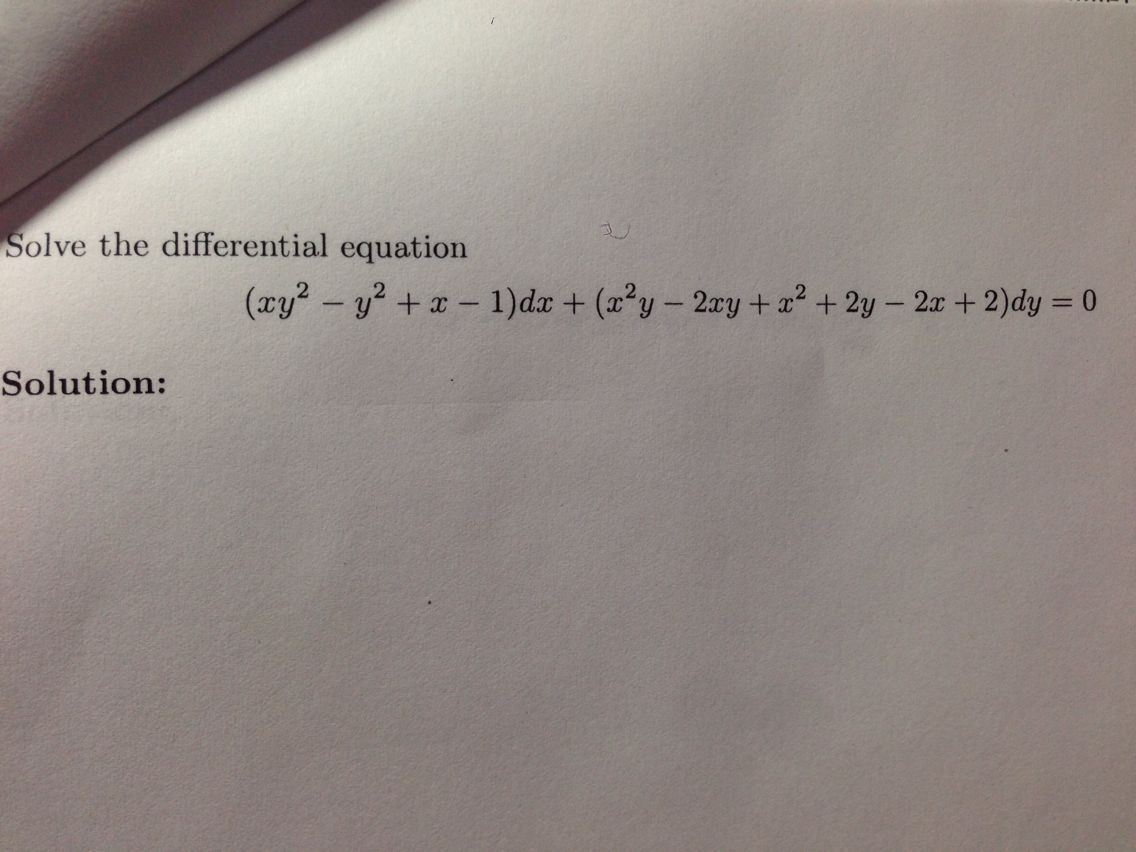 | |
 |  |  |
「(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
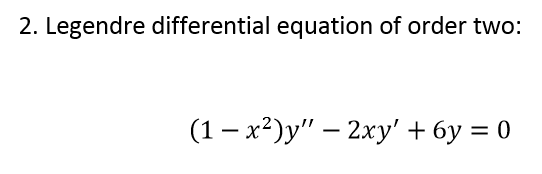 |  |  |
 | ||
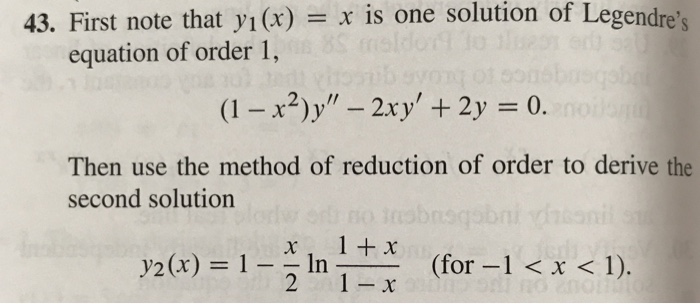 |  | |
「(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | 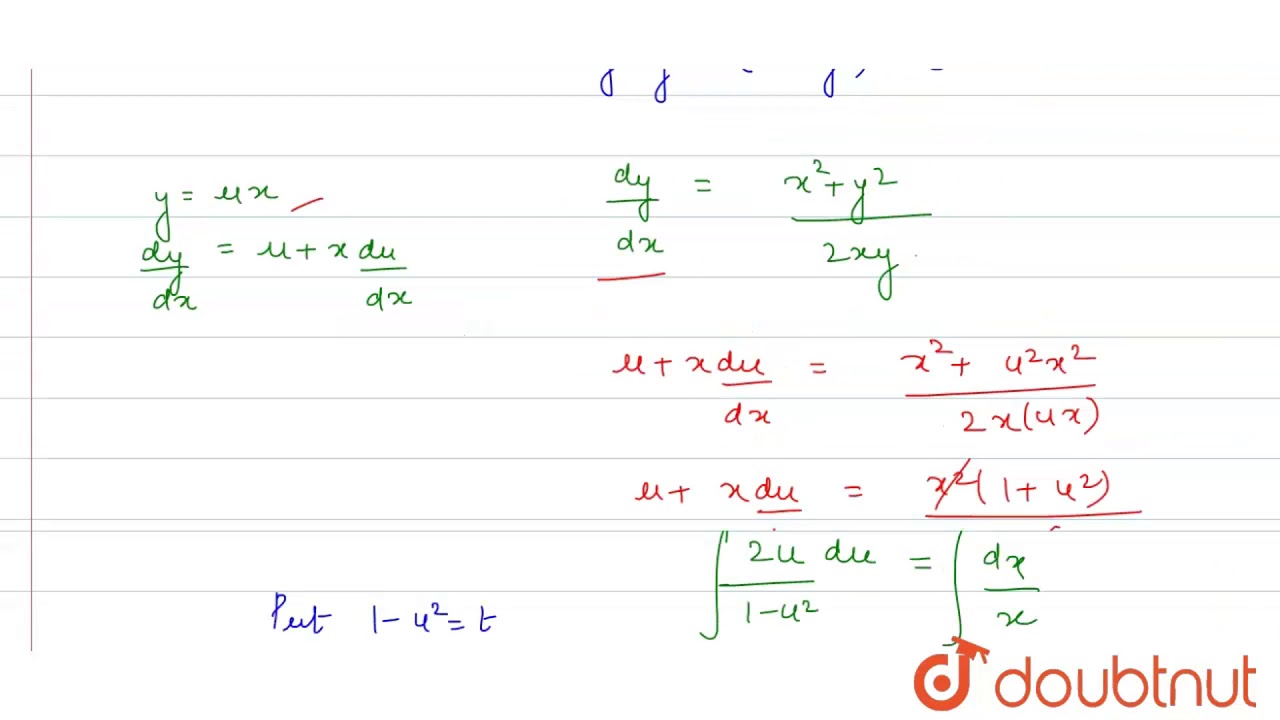 | |
「(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
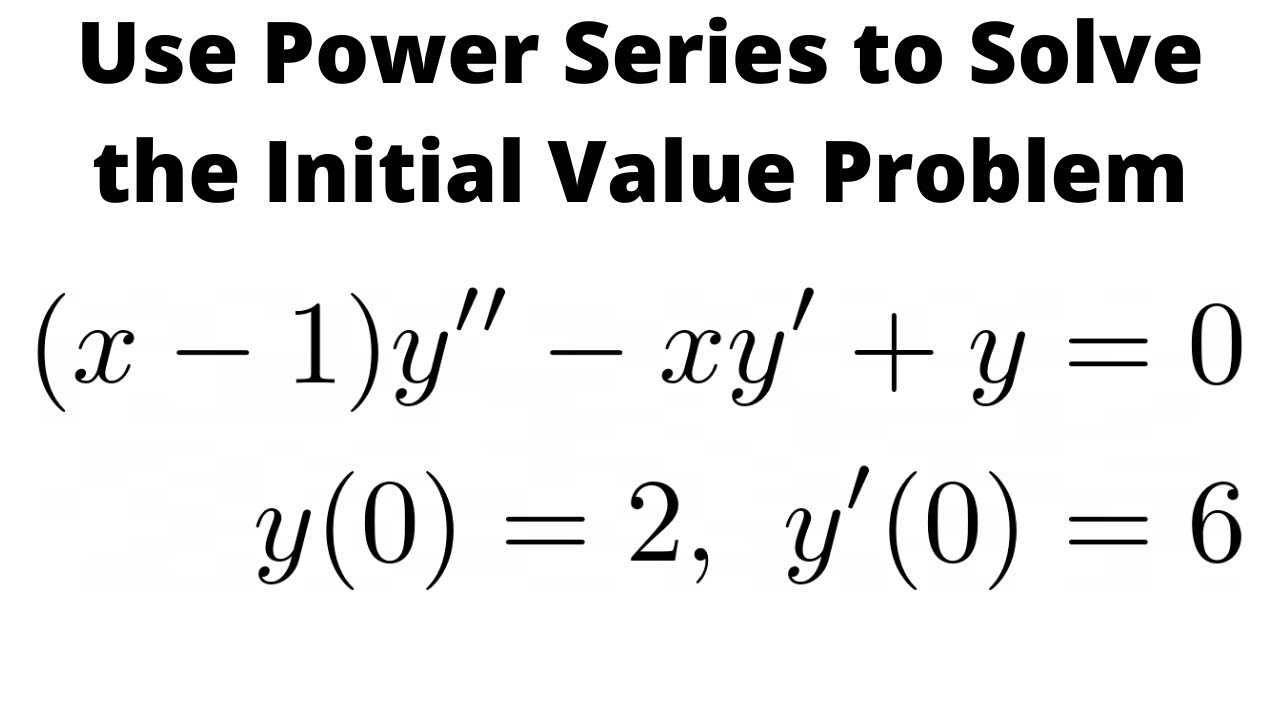 | 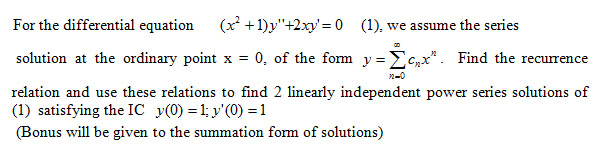 |  |
 |  |  |
「(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
「(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
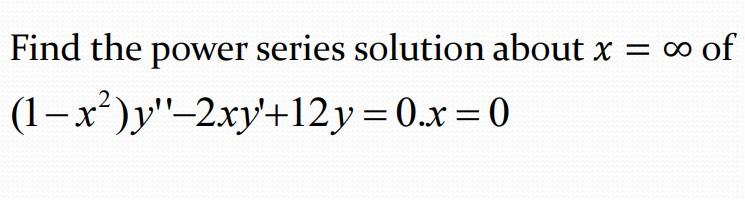 |  |  |
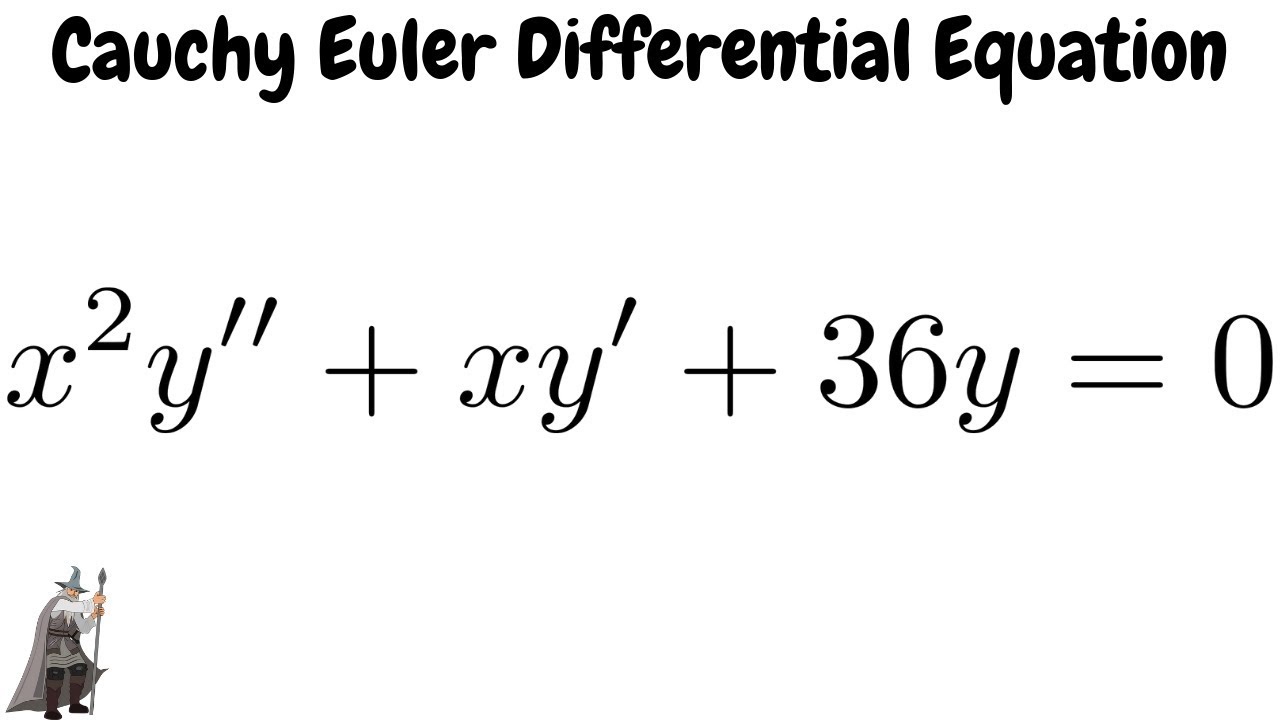 | ||
 | 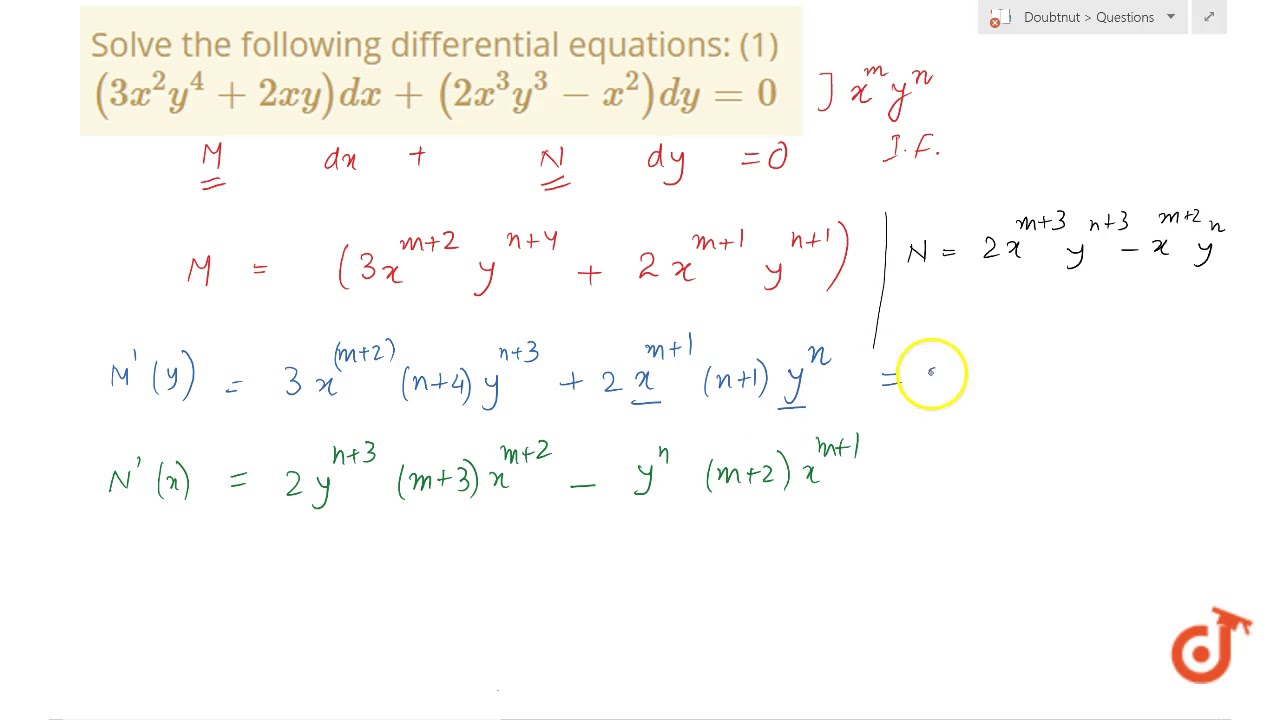 | |
 |  |  |
「(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | 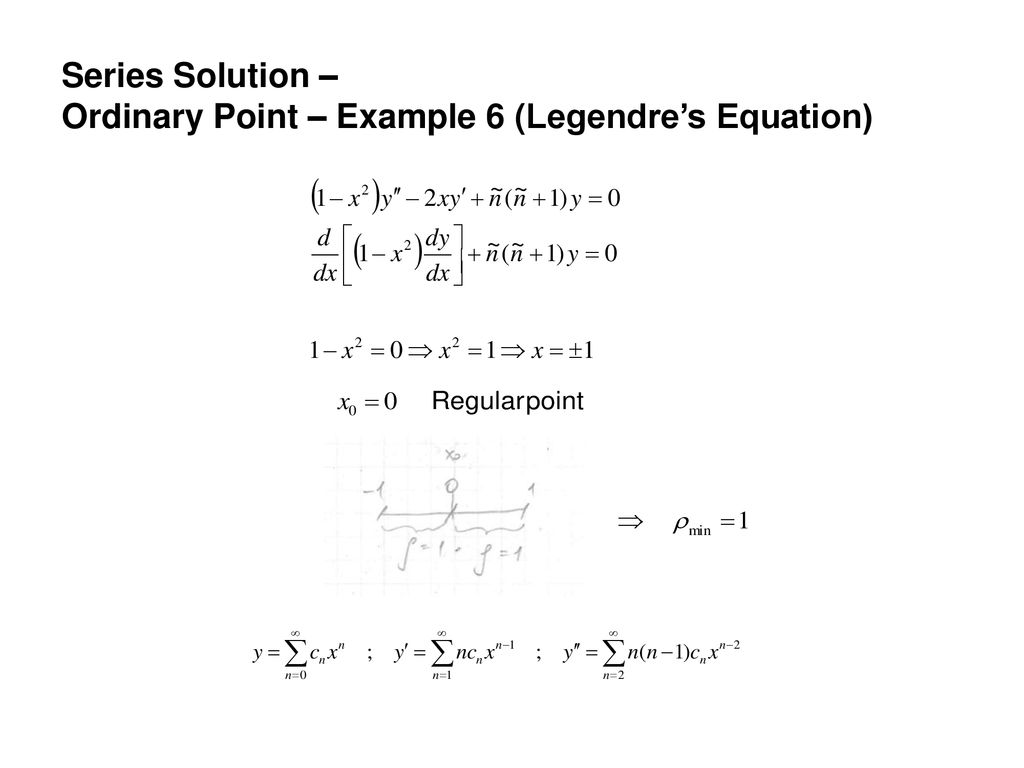 | |
「(1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 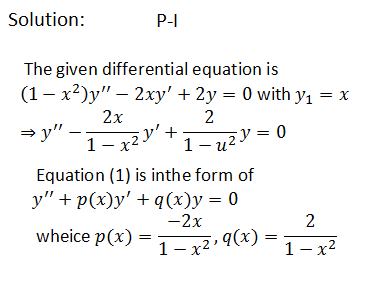 |  |
 |  | |
 |  |
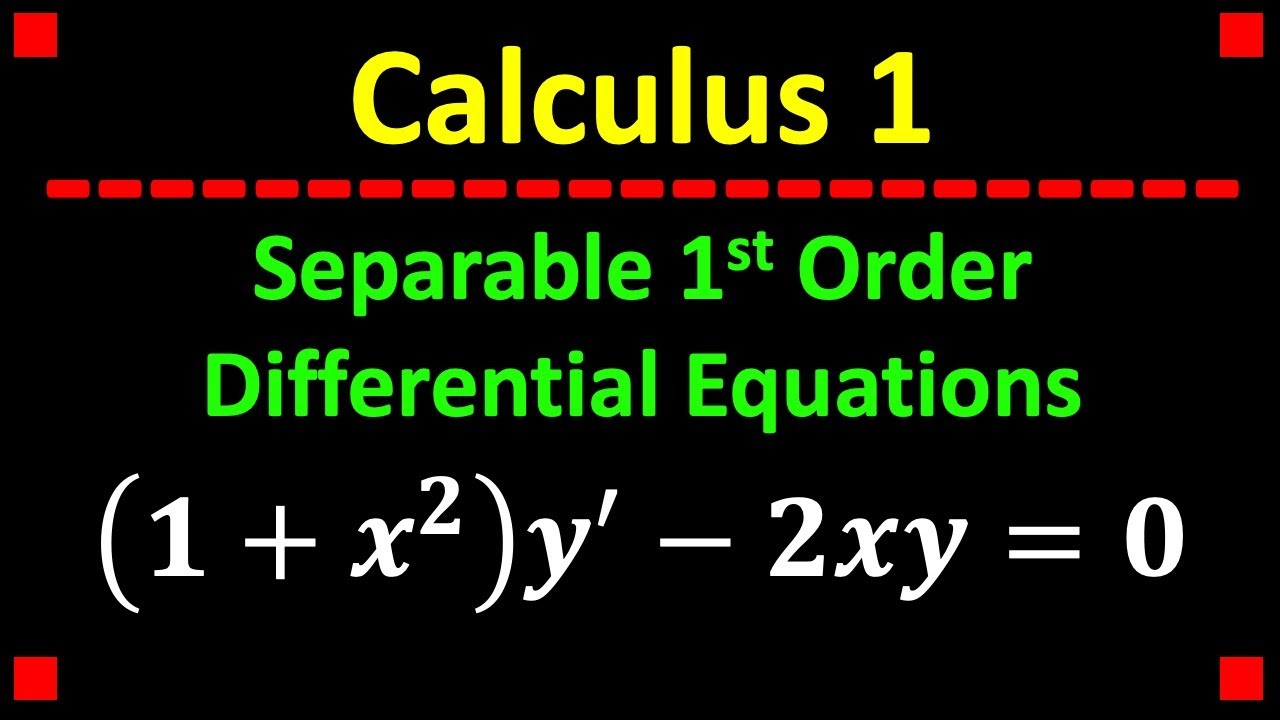
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback I wasn't sure if I could, but I went ahead and integrated both sides with respect to x to get y ′ 2 y x 1 − x 2 = C 1 I then assumed C 1 = 0 to turn it into a separable differential equation because I don't know what to do with the above expression and , as expected, upon checking, this was the incorrect answer
Incoming Term: (1+x^2)y'-2xy=0, (1-x^2)y''-2xy'+2y=0, (1-x^2)y''-2xy'+2y=0 power series, (1-x^2)y''-2xy'+6y=0, (1-x^2)y''-2xy'+12y=0, (1-x^2)y''-2xy'+2y=0 chegg, (1-x^2)y''+2xy'=0 y1=1, (1-x 2)y''-2xy'+2y=0, (1-x^2)y''-2xy'+n(n+1)y=0, (1-x^2)y''-2xy'+2y=0 y1=x,




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿